Wild or cultivated biodiversity?
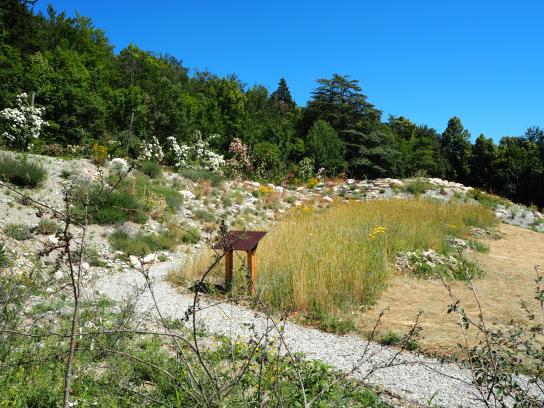

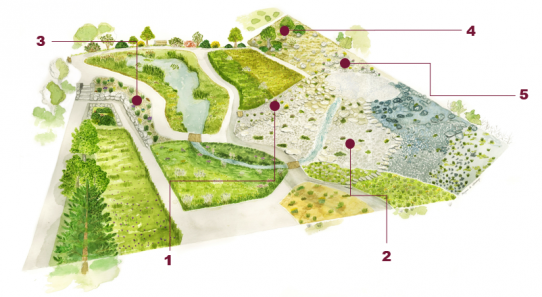
Dry chalky soils - "Pentes sèches"
In mediterranean and alpine climates, superficial, quick-draining and highly eroding soils are colonized by garrigues and heaths. They are dominated by ash-coloured brooms and common lavandulas.
Unstable screes lie on the steepest and most exposed slopes. There, the vegetation is constantly rejuvenated and composed by tall plants where Calamagrostis varia dominates.
Unstable screes lie on the steepest and most exposed slopes. There, the vegetation is constantly rejuvenated and composed by tall plants where Calamagrostis varia dominates.
1 : Calcareous slope from the Mediterranean to the mountane zone
2 : Calcareous slope from the subalpine and the alpine zones
3 : Blue oat grass
4 : Juniperus sabina scrub
5 : Supra-Mediterranean garrigue
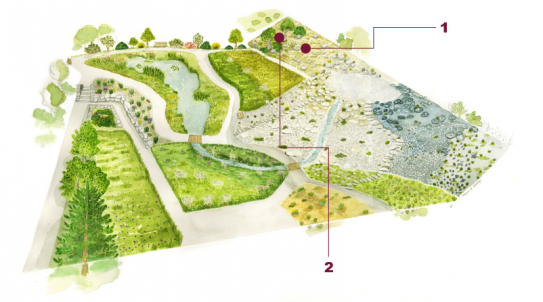
Steppic grasslands - "Pelouses steppiques"
In the Alps steppic grasslands, which are related to Eastern European steppes, are confined into the internal valleys. These habitats have a pronounced continental climate and poor, superficial soils. Low, open and discontinuous, they are composed of perennial tufted grasses and bushes (perennials chamaephytes). They evolve into steppic heaths when they are colonized by trailing bushes or trees.
1 : Central alpine arid grassland (Stipa capillata and Poa perconcinna)
2 : Juniperus sabina scrub
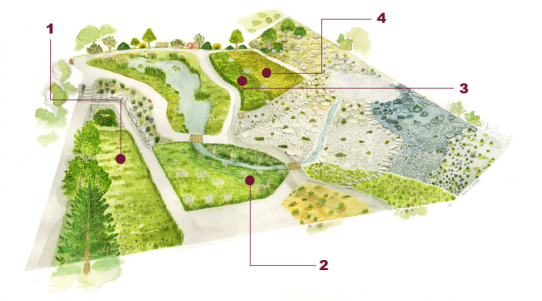
Cultivated environments - "Milieux cultivés"
Cultivated environments are part of the agricultural landscapes of the Alps.
Mowed grasslands are tall herbaceous formations dominated by grasses. They can be either semi-natural, usually rich in species, or man-made and used for fodder. When winter cereal crops (wheat, barley, oat, etc.) are not treated with or seldom treated with pesticides, they host messicole plants (‘harvest’ plants), which attract pollinating insects.
Mowed grasslands are tall herbaceous formations dominated by grasses. They can be either semi-natural, usually rich in species, or man-made and used for fodder. When winter cereal crops (wheat, barley, oat, etc.) are not treated with or seldom treated with pesticides, they host messicole plants (‘harvest’ plants), which attract pollinating insects.
1 : Lowland hay meadow dominated by Arrhenatherum elatius
2 : Medio-european humid grassland on basic and oligotrophic soil
3 : Semi-dry calcareous Bromopsis erecta grassland
4 : Arable land with unmixed crops grown by low-intensity agricultural methods